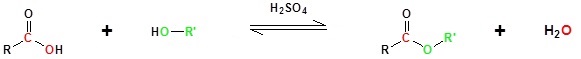
Fischer esterification or Fischer-Speier esterification is a type of esterification reaction done by refluxing a carboxylic acid and an alcohol with an acid catalyst present. As the equation below illustrates, the reaction forms an ester and water as products. Fischer esterification was first described in 1895 by Emil Fischer and Arthur Speier
1. The acid catalyst protonates the carbonyl oxygen, increasing the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon
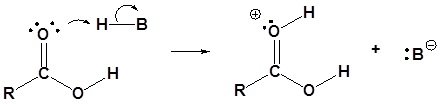
2. The nucleophilic oxygen atom of the alcohol attacks the carbonyl carbon, giving an activated complex
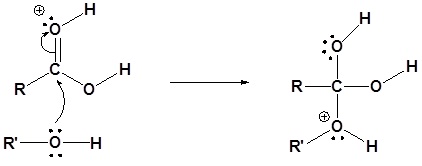
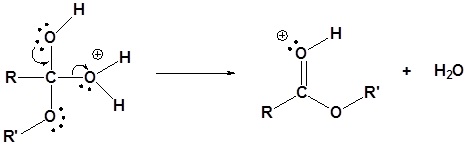
3. A proton is transferred from the activated complex to one of the hydroxy groups, giving a new oxonium ion
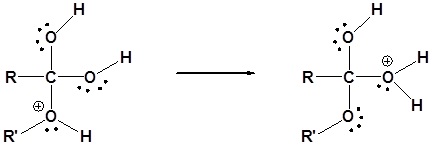
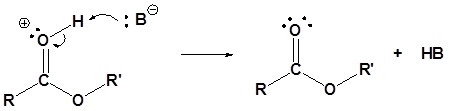
4. The newly protonated oxonium ion departs the activated complex as a neutral water leaving group